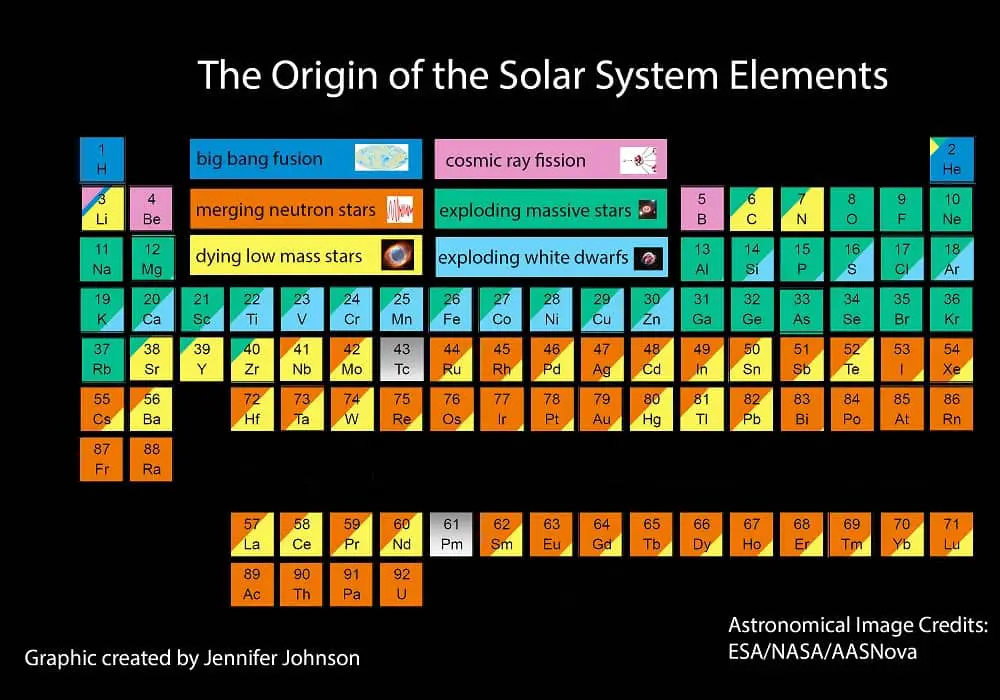
Astronomer has created a sensational new periodic table that explains the
origin of nearly everything. The periodic table illustrates how elements were
created from different processes in the universe like the merging neutron
stars—how Francium was made, exploding mass stars—how neon was crafted, and
dying low mass stars—which helped make other elements like strontium.
Jennifer A
Johnson has taken the periodic table to a whole other level by implementing a
creative twist to the periodic table: The astronomer highlighted the origin of
each element, completely changing the perspective of everything that is around
us.
As it is
explained, an average human is made up of around seven OCTILLION—Yup that’s a
number and it’s this: 7,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000— atoms, most of
which are HYDROGEN.
Johnson explains it, hydrogen is in fact the most COMMON element in our
universe and is believed to have been created by th4e Big Bang around 13.4
BILLION years ago.
Ms. Johnson, the other elements were created from different processes in the
universe like the merging neutron stars—how Francium was made, exploding mass
stars—how neon was crafted, and dying low mass stars—which helped make other
elements like strontium.
This
revolutionary yet fascinating project was born from frustration says, Dr.
Johnson.
blog post for the Sloan digital Sky Survey Dr. Johnson said: “This is what
happens when you give two astronomers, who are tired of reminding everyone
about which elements go with which process [on] a periodic table, a set of
markers, and time when they should have been listening to talks.”
at the bottom of the section, several elements have been left off the list.
Dr. Johnson
says that: “Tc, Pm, and the elements beyond U do not have long-lived or stable
isotopes. I have
ignored the elements beyond U in this plot, but not including Tc and Pm looked
weird, so I have included them in gray.”
similar project was even uploaded to Wikipedia, however, Dr. Johnson notes that
some of the information on that table is incorrect.
“High-mass
stars end their lives (at least some of the time) as core-collapse supernovae.
Low-mass stars usually end their lives as white dwarfs. But sometimes, white
dwarfs that are in binary systems with another star get enough mass from the
companion to become unstable and explode as so-called Type-Ia supernovae,”
wrote Dr. Johnson.
“Which
‘supernova’ is being referred to in the Wikipedia graphic is not clear. The
information for Li is incorrect. [The isotope] Li is indeed made by cosmic rays
hitting other nuclei and breaking them apart.”
“But most of
the far more common Li isotope is without question made in low-mass stars and
spewed out into the Universe as the star dies. Some Li is also made in the Big
Bang, and a small fraction by cosmic ray fission,” added Dr. Johnson.
table.