You may contemplate that as you are reading this, your body in a stationary position. But, everything inside the universe travels, from our planet (Earth) –which revolves on its axis at a speed of approximately 1700 km/h— to the solar system and even the Milky Way Galaxy.
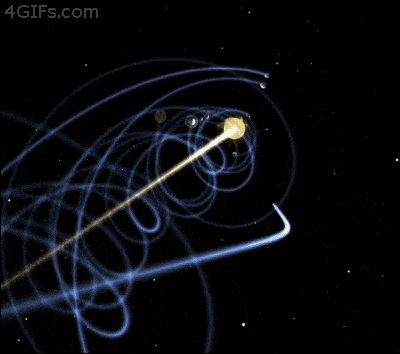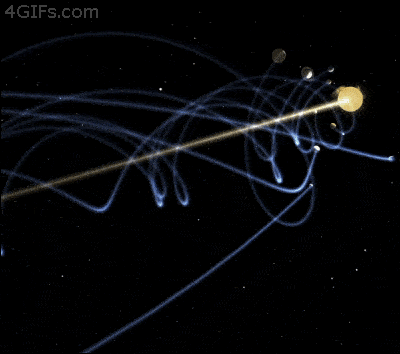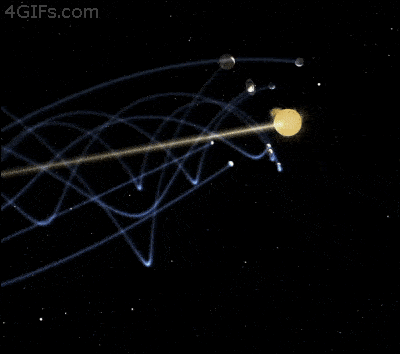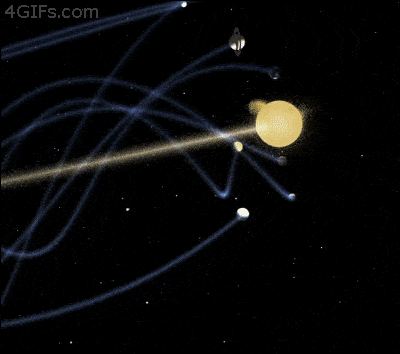
All the planets in the solar system and their personal moons also travel through space. Actually, in order to retain a stable orbit, it is essential for Earth to move around 30 km/s. The innermost planets in our system, Mercury and Venus travel faster while planet Mars and the external planets of our solar system fly through space at a sluggish pace.
But think superior and bigger. Even yet the Sun is at the heart of our solar system, it is also travelling at an unbelievable speed through space.
If we consider even bigger, we will understand that even our gigantic Milky Way galaxy is in motion, and all continuing things that make up the universe such as stars, gas clouds, planets, black holes and even the mighty dark matter travel within the universe.
If we consider even bigger, we will understand that even our gigantic Milky Way galaxy is in motion, and all continuing things that make up the universe such as stars, gas clouds, planets, black holes and even the mighty dark matter travel within the universe.
Just as Earth revolve around the Sun and our Sun revolves the galactic center –which from our vantage point is situated around 2500 light-years away— in an elliptic trajectory. It finishes a revolution every 225 million years roughly. This is known as a Galactic year.
It is predicted that since the Sun and Earth came into being, 20 galactic years have passed, which means that we ended 20 successful revolutions orbiting the galactic center. However, if we relate detailed human history to our movement through the universe, we would understand we hardly moved in our galactic path.
However, the Milky Way Galaxy isn’t motionless or stationary, and it also moves through the universe. So is there anything to which its motion can be compared?
For a long period time, astronomers and scientists were not able to answer any questions like this. We can compare our galaxy’s speed with other galaxies, but all the other galaxies travel through the universe just as the Milky Way Galaxy does. In order to answer this mystery, astronomers and scientists point towards the CBR (Cosmic Background Radiation) and the Big Bang. As stated by NASA, The Big Bang theory guesses that the early universe was an extremely hot place and that as it grows; the gas within it gets cooler. Therefore the universe should be packed with radiation that is exactly the remnant heat left from the Big Bang, called the “Cosmic Microwave Background,” or CMB. The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation was produced 13.7 billion years ago. Theoretically speaking, the CBR suggests experts with a frame of reference for the entire universe, compared to which we can determine and calculate our motion. In order to get knowledge of how fast we’re travelling through the universe, astronomers need to take away the motion of planet Earth around the Sun and the Sun around the center of the Milky Way from the movement measured compared to the Cosmic Microwave Background (CBR) This means that the Milky Way Galaxy is travelling through space at an amazing speed of 2.1 million km/h, in the direction of the constellations of Virgo and Leo; exactly where the so-called Great Attractor is situated.

