New research published few days ago titled “Globally distributed subducted materials along the Earth’s core-mantle boundary: Implications for ultralow velocity zones” has revealed a fascinating discovery about the composition of the Earth’s core-mantle boundary.
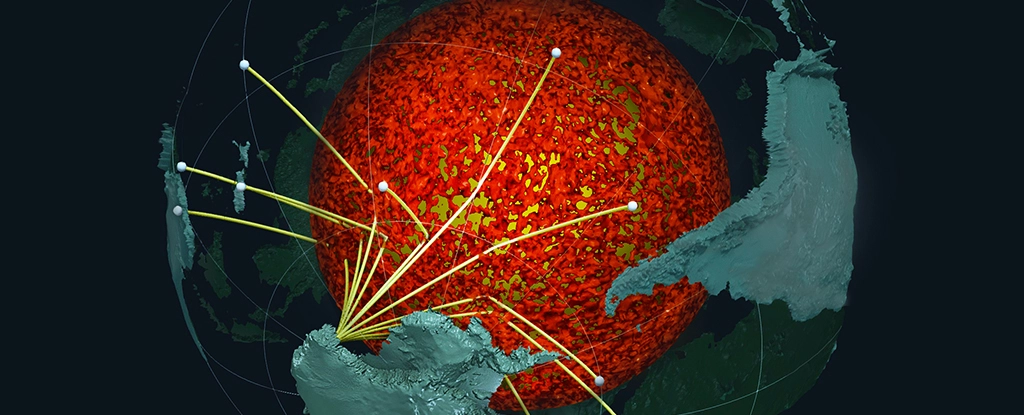
Table of Contents
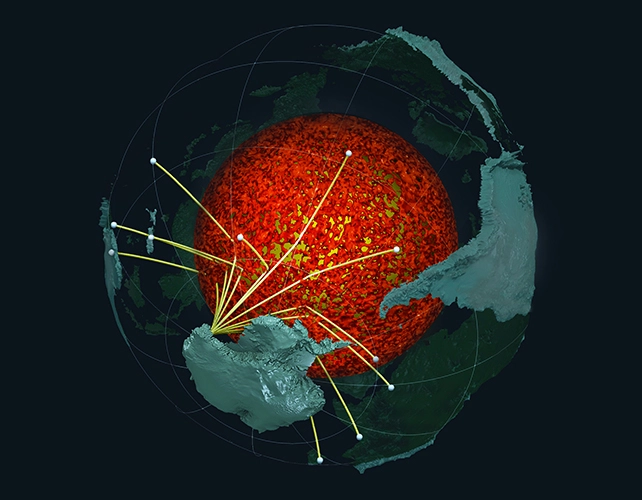
The study suggests that beneath the Earth’s surface, ancient ocean floor materials likely surround the core, providing crucial information about the Earth’s structure and dynamics.
Unravelling the Mystery of Ultralow Velocity Zones
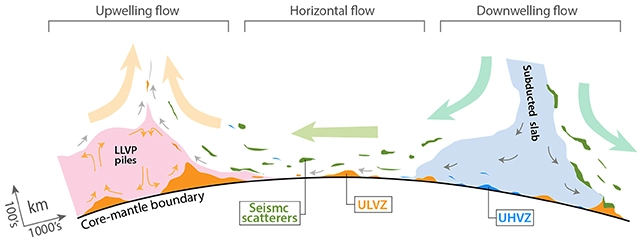
Ultralow velocity zones (ULVZs) have long been a topic of interest for geophysicists. These mysterious regions are characterized by a significant reduction in seismic wave velocities, indicating the presence of distinct materials at the boundary of the Earth’s core and mantle. The recent study sheds light on the possible composition of these enigmatic zones, offering a clearer understanding of the Earth’s interior.
Subducted Materials and the Core-Mantle Boundary
The research paper proposes that ancient ocean floor materials, which have undergone subduction, are now distributed along the Earth’s core-mantle boundary. This discovery has significant implications for our understanding of the geological processes that occur beneath the Earth’s surface, such as the recycling of the Earth’s crust and the formation of mantle plumes.
Implications for Earth’s Dynamics and Evolution
The presence of subducted ocean floor materials at the core-mantle boundary may help to explain the unique behavior of Earth’s mantle and the generation of the planet’s magnetic field. Furthermore, this finding could provide valuable insights into the long-term evolution of the Earth’s interior, as well as the processes that have shaped its surface over billions of years.
A Fascinating Intersection of Geophysics and Earth History
The discovery of ancient ocean floor materials surrounding the Earth’s core marks a significant advancement in our understanding of the planet’s structure and dynamics. This research not only elucidates the composition of mysterious ultralow velocity zones but also offers a glimpse into the deep history of the Earth, revealing the intricate interplay between geophysical processes and the Earth’s evolution.
References:
Research Paper: Globally distributed subducted materials along the Earth’s …

