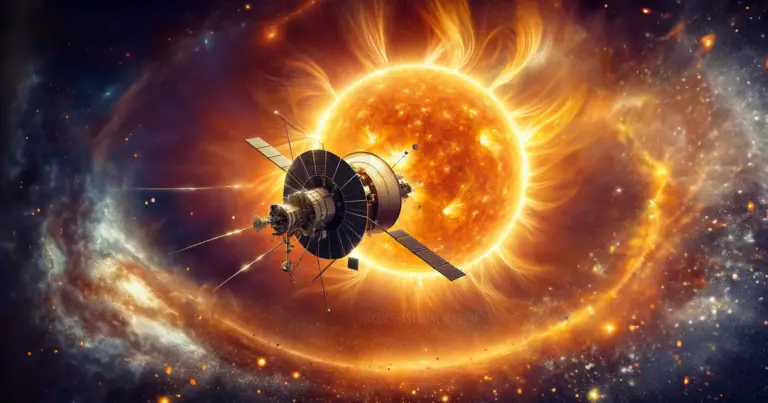
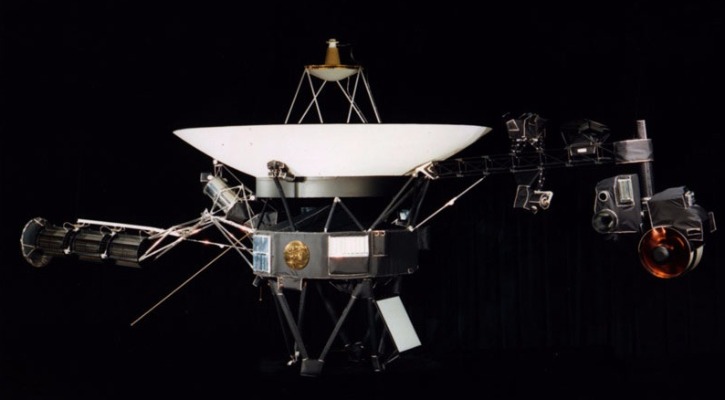
In a mission that pushes the boundaries of human ingenuity and space exploration, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe is gearing up for an unprecedented close encounter that’s being titled as ‘Touch The Sun’ with the Sun this year.
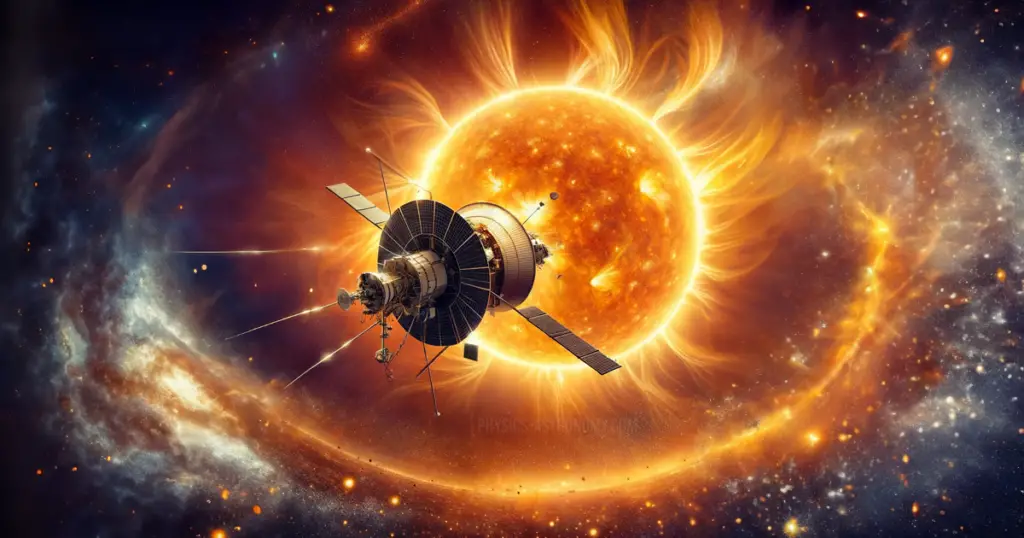

This daring mission will see the probe rapidly soar through the Sun’s upper atmosphere, known as the corona, marking a significant milestone in our understanding of our host star.
The Parker Solar Probe’s journey to the Sun is not just a feat of engineering; it represents a crucial step in unraveling the mysteries of the Sun and its influence on the entire solar system. Much like the moon landings provided insights into the moon’s origin and geological history, analyzing the components that make up the Sun is vital for understanding its behavior and impact on the solar system.
In December 2021, NASA announced a historic achievement: for the first time, a spacecraft had made contact with the Sun by flying through its corona. This momentous event marked a significant advancement in solar science, as the probe collected essential data on charged particles and magnetic fields. These findings are crucial for understanding solar phenomena like solar flares and coronal mass ejections, which can have profound effects on Earth and other planets in the solar system.
The Parker Solar Probe’s mission is not only about gathering data but also about testing the limits of space technology. The probe is equipped with cutting-edge instruments and a heat shield designed to withstand the extreme temperatures and radiation near the Sun. As it zips past the Sun at a staggering speed of 435,000 mph, the probe will provide unprecedented close-up observations of the solar atmosphere.
The significance of this mission extends beyond the realm of solar physics. By studying the Sun’s corona, scientists hope to gain insights into fundamental processes that occur in stars throughout the universe. The data collected by the Parker Solar Probe will also help improve our ability to forecast space weather events, which can disrupt satellite communications, navigation systems, and power grids on Earth.
As the Parker Solar Probe prepares for its close encounter with the Sun, it stands as a testament to human curiosity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. This mission not only deepens our understanding of the Sun but also inspires future generations of scientists and explorers to continue exploring the vast and mysterious cosmos.
The Parker Solar Probe’s journey to ‘touch’ the Sun is a reminder of the incredible achievements possible when we dare to explore the unknown. As we await the probe’s historic rendezvous with the Sun, we stand on the brink of a new era in solar science, one that promises to shed light on some of the most enduring mysteries of our star and the universe at large.